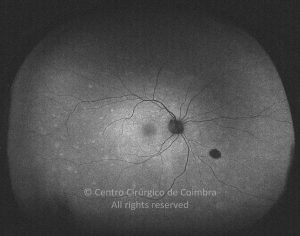
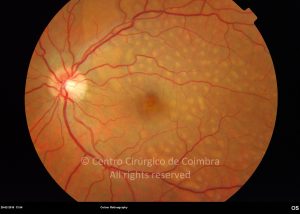
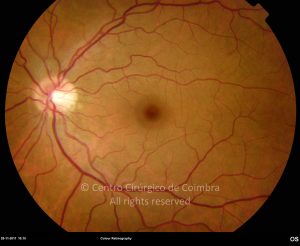
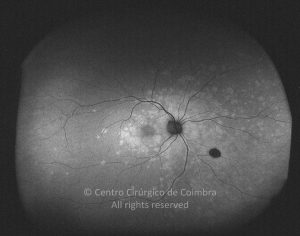
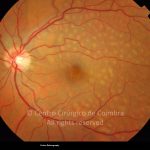
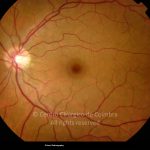
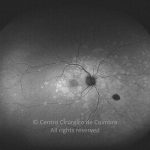
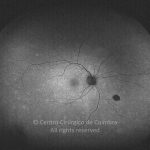
A síndroma de múltiplas manchas brancas evanescentes é uma retinopatia aguda, multifocal e geralmente unilateral, que é predominantemente observada em mulheres saudáveis com 20-30 anos de idade.
Os doentes apresentam visão central desfocada, fotópsias, escotomas paracentrais ou aumento da mancha cega e, ocasionalmente cefaleias.
Esta síndroma é caracterizada por múltiplas manchas pequenas branco-acinzentadas, ao nível do epitélio pigmentado da retina, no polo posterior e poupando a fóvea.
As manchas brancas desaparecem espontaneamente em 2 meses.
Diagnóstico Diferencial
- Neurorretinopatia macular aguda
- Epiteliopatia Pigmentar Placóide Multifocal Posterior Aguda
- Epitelite Pigmentar Retiniana Aguda
- Retinopatia Externa Oculta Zonal Aguda
- Retinocoroidopatia de Birdshot
- Neurorretinite unilateral difusa aguda
- Toxoplasmose