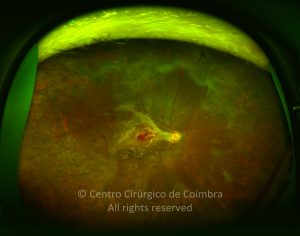
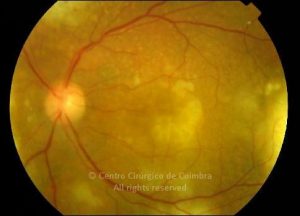
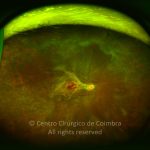
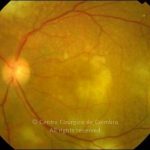
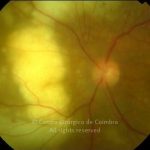
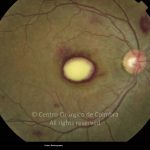
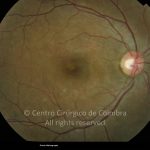
O espectro dos tumores linfóides intraoculares abrange desde as hiperplasias linfóides reativas a vários tipos de linfomas malignos primários ou secundários.
O linfoma intraocular primário é geralmente um linfoma de células B, não-Hodgkin, do olho e do SNC.
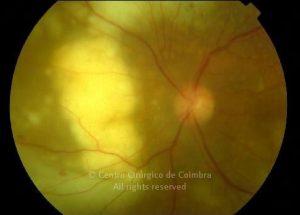
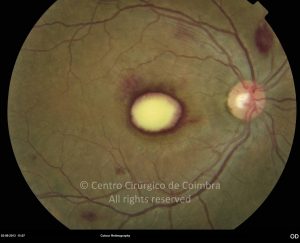
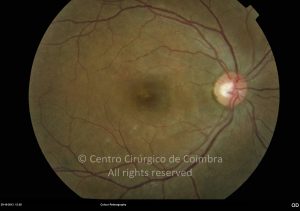
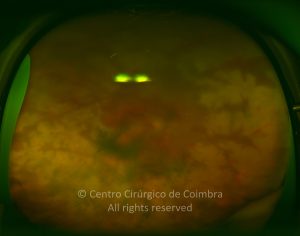
As manifestações oculares incluem aglomerados de células no vítreo e lesões multifocais infiltrativas, grandes, amareladas, sub-retinianas e sub-EPR.
Os linfomas intraoculares podem ser classificados em vários subgrupos:
– Linfoma intraocular primário (da retina e vítreo)
– Linfoma primário da úvea
– Linfoma secundário
DIAGNÓSTICO DIFERENCIAL do linfoma intraocular/SNC