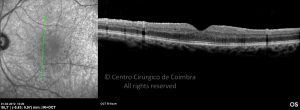
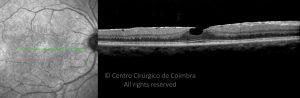
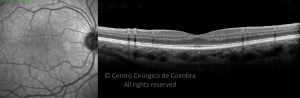
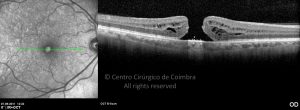
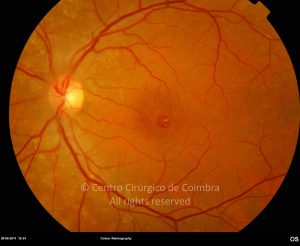
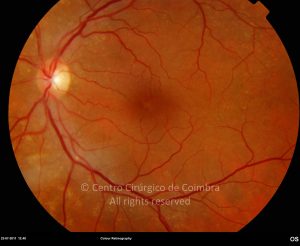
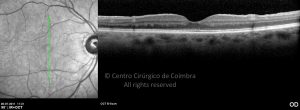
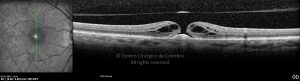
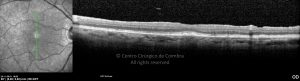
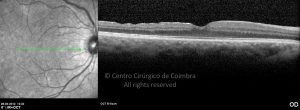
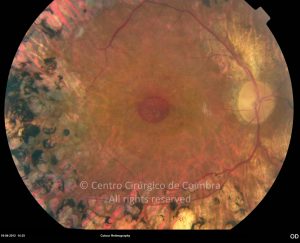
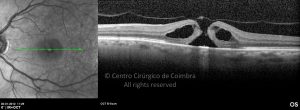
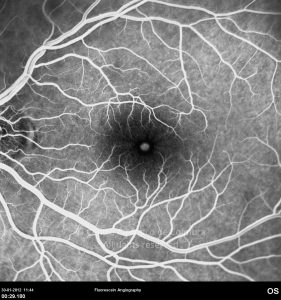
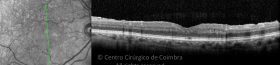
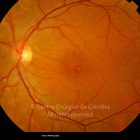
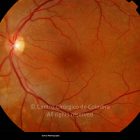
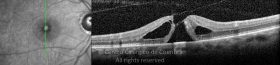
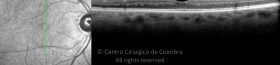
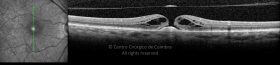
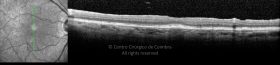
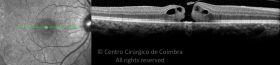
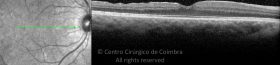
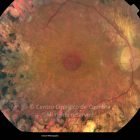
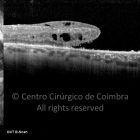
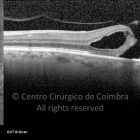
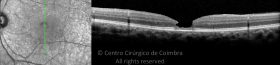
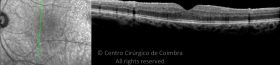
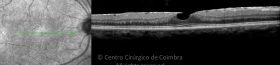
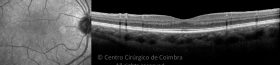
Um buraco macular é uma abertura anatómica ou deiscência da retina, na fóvea.
Pode ser idiopático ou secundário a traumatismo, queimaduras acidentais da fóvea por laser, edema macular cistoide de longa duração e miopia.
A fisiopatologia exata da formação destes buracos permanece desconhecida. A formação de membranas epirretinianas, tração vítrea e forças hidráulicas parecem desempenhar um importante papel em alguns casos. As trações vítreo-foveolares antero-posteriores e as trações centrífugas exercidas por membranas epirretinianas em redor da fóvea são, na clínica, as causas prováveis desta patologia.
Diagnóstico Diferencial
- Retinopatia serosa central
- DMI
- Edema macular cistoide
- Membrana epirretiniana com pseudo-buraco
- Buraco lamelar
- Retinopatia solar
- Drusas
- Tração vítreomacular