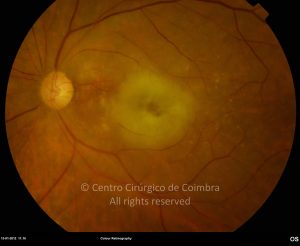
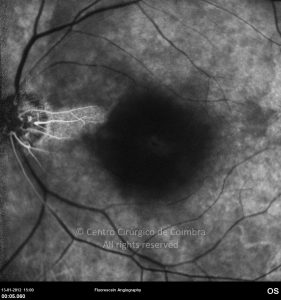
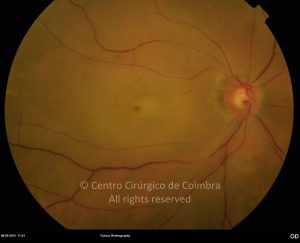
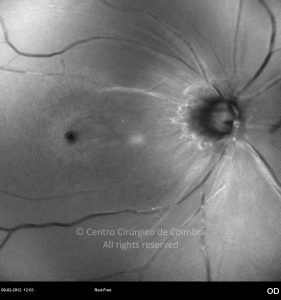
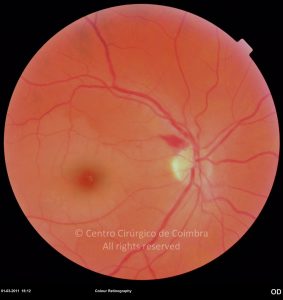
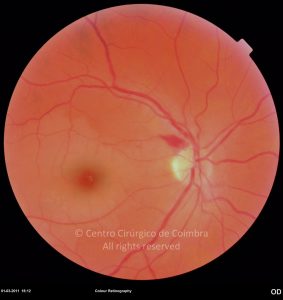
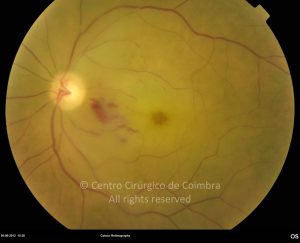
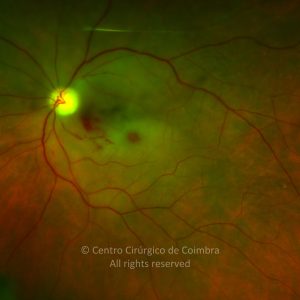
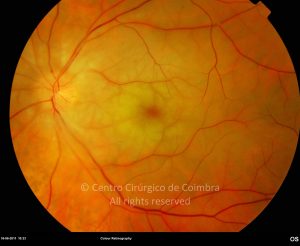
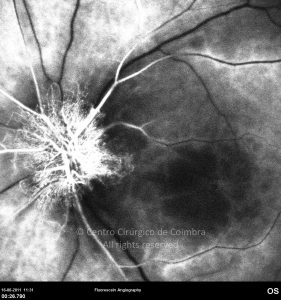
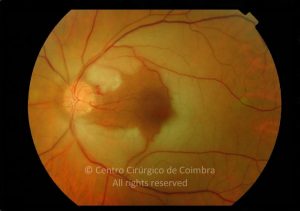
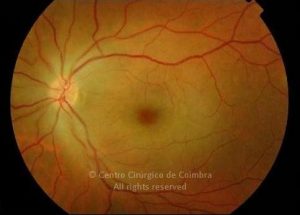
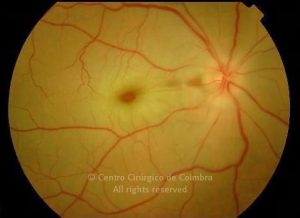
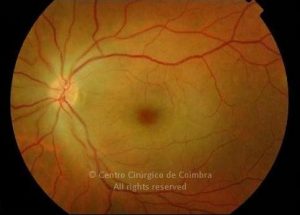
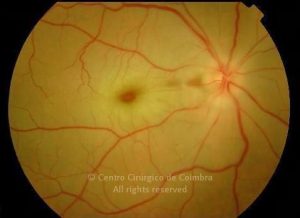
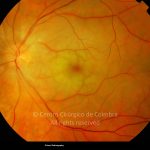
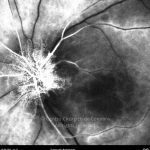
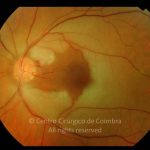
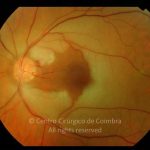
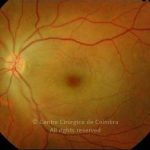
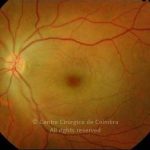
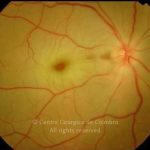
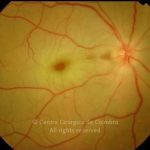
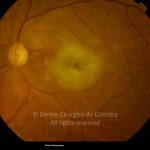
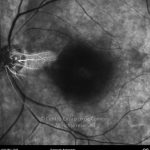
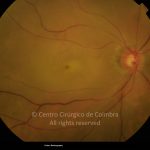
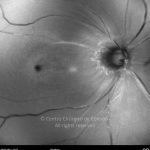
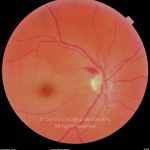
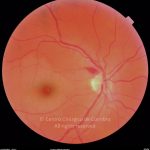
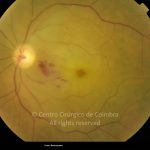
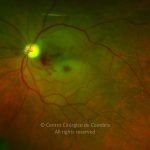
A oclusão aguda da artéria central da retina provoca uma perda súbita da visão.
Na fase aguda, a retina no polo posterior perde a sua transparência e adquire um aspeto esbranquiçado. Uma mancha de cor vermelho-cereja está presente na fovéola.
O processo fisiopatológico responsável pela oclusão da artéria central da retina pode incluir as seguintes situações:
- Colapso circulatório
- Aneurisma dissecante
- Embolia
- Hemorragia sob uma placa aterosclerótica
- Necrose hipertensiva arterial
- Trombose luminal
- Espasmo
- Vasculite
Anomalias sistémicas podem ser encontradas em 90 % dos doentes afetados:
- Doença valvular cardíaca
- Aterosclerose carotídea
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hipertensão arterial sistémica