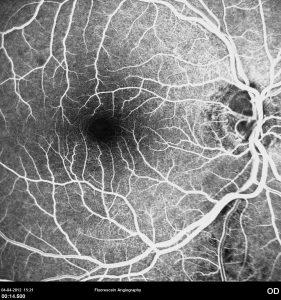
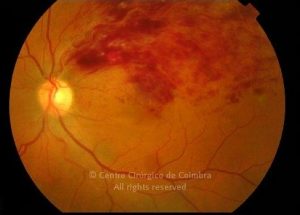
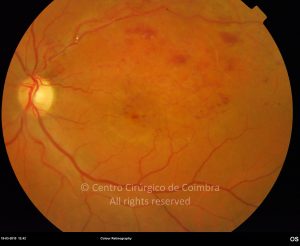
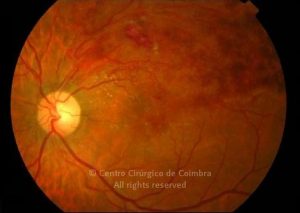
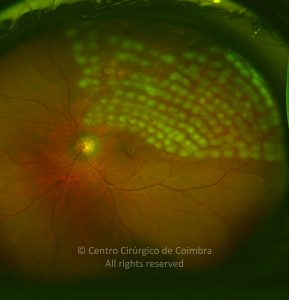
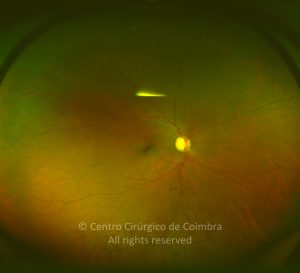
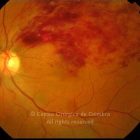
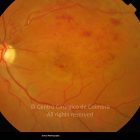
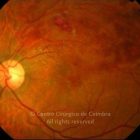
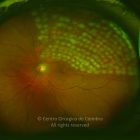
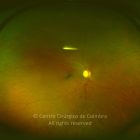
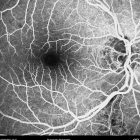
A oclusão de ramo da veia central da retina é caracterizada pela dilatação e tortuosidade da veia afetada, associada com hemorragias retinianas, manchas algodonosas e edema retiniano da área drenada pela veia.
É geralmente causada por um trombo nos cruzamentos arteriovenosos, onde uma artéria espessada comprime a parede da veia subjacente.
As complicações da oclusão de ramo da veia que são mais comuns e potencialmente limitantes da visão, incluem o edema macular e a neovascularização da retina.
Diagnóstico Diferencial
- Retinopatia diabética
- Retinopatia hipertensiva
- Leucemia
- Síndroma de isquemia ocular
- Edema do disco óptico
- Anemia
- Retinopatia por estase venosa